Mr. Xie is usually busy with work and often goes abroad for negotiations. With the strong arrangement of his wife, he went to Beitou Health Management Hospital for painless stomach intestine last month. After 3 days of low residue and clearance of t...
Mr. Xie is usually busy with work and often goes abroad for negotiations. With the strong arrangement of his wife, he went to Beitou Health Management Hospital for painless stomach intestine last month. After 3 days of low residue and clearance of the kidney, a 1.2 cm glandular polyps were found to be removed immediately. He hurried to a venue in the evening and drank a few cups. When he got home, he felt bleeding stools?
The cancer rate of brain cancer is the highest among people in China. The idea of taking painless stomach lenses to prevent cancer is gradually rising. However, should I find that polyps should not be removed? Do you want to cut it on the spot? Does it hurt? Can you return to normal diet after cutting? …....has been the most common question for our internal visual center education? Let’s give you an explanation!
Q: Do you have to cut the polyps?
A: Large brain polyps are roughly divided into hyperplastic polyps and adenomatous polyps. Due to the occurrence of more than 90% of the brain cancer, it is caused by the malicious evolution of large brain adenomatous polyps over about 10 years. Removing large brain adenomatous polyps can reduce the occurrence of large brain cancer by 76 to 90% and reduce the mortality rate of large brain cancer by 50%. Therefore, during the examination of the large brain lens, if the large brain polyps are found, especially the adenomatous polyps, it is best to remove them, so as to avoid the polyps growing and becoming large brain cancer as the polyps grow.
Based on the analysis of these healthy or healthy recipients in our hospital, nearly 40% of the people have adenoma, and nearly 50% of the people have adenomas. Among them, advanced adenomas (advanced adenomas that are more than one centimeter of adenomas, or have hairy adenomas, or have abnormal cell differentiation) accounted for about 7 to 8%.
Q: Does it hurt to remove polyps?
A: Basically, there will be no feeling when removing the polyps from the large brain, because the nerves of the stomach tract are located on the deeper muscle level, and polyps removal is usually only in the surface organization, so even if anesthesia and sleep-sleeping internal lens examination is not performed, it will not cause pain.
Q: What are the methods to remove polyps?
A: Basically we will decide based on the size of the polyp. Usually, polyps that are less than 0.5 cm can be removed by biopsy forces; if they are more than 0.5 cm, we will take polypectomy or endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). This is a method of using a snare to cover the polyps and then firing the polyps. After removal, the wound size will be used to close the wound with the hemostasis clamp to avoid bleeding.
Q: What should you pay attention to after cutting?
A: According to current medical technology, slicing or resection of polyps is a very mature treatment method. The risk of bleeding of polyps less than one centimeter is less than 2%. Some larger wounds can also close the wound with the hemostasis clamp to reduce bleeding. Generally speaking, the wound that was removed will be scabbed within 5 to 7 days, and the hemostasis clamp will also be discharged and discharged, so there is no need to worry about staying in the body. However, during this period before the hemostatic cervical falls, we still hope that the examinee can cooperate with the following:
(1) Do not lift heavy objects, climb mountains, or exercise vigorously for one week - climbing is actually good. Hemostatic cervical lifting and intense exercise can easily cause abdominal pressure to increase, causing the hemostatic cervical falls.
(2) Do not drink alcohol or eat raw food for a week; this is because alcohol can stimulate the gastric mucosa of the kidneys and gastric mucosa. Raw food may contain bacteria. In addition, crude celery and nipples can cause a lot of stool and rub the wound. Be careful.
(3) Avoid riding a flight within 5 days, especially those who use hemostasis clamps. The aircraft is closed and lifted into the air, which will affect the absorption of gas in the kidneys and increase the pressure of the kidneys and affect the wound.
(4) When you go home after surgery, you should pay attention to the stool. You should rest more on the day. In fact, it is normal for a few days before the stool is removed. As long as the blood volume gradually decreases, it doesn't matter. You should pay attention unless the bleeding continues, or you only relieve blood but not relieve it. It may also be caused by hemorrhoids. Once bleeding occurs, the doctor will evaluate the condition and give the drug treatment, or conduct internal lens inspection and treatment.
(5) After the swelling meat is removed, the anticoagulant should be stopped for another 5-7 days according to the doctor's instructions to avoid affecting the coagulation function..
Endoscopic mucosal reaction (EMR) procedure explained
1. Intra-black lens detects a 1.2 cm adenomatous polyps 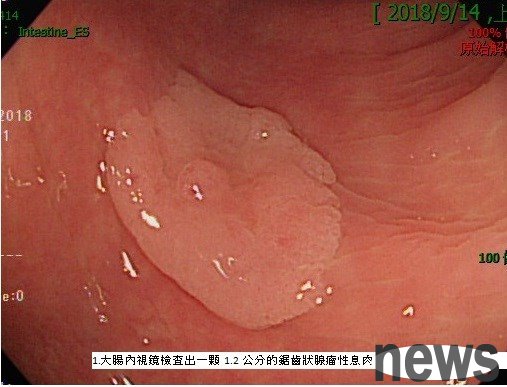
2. Narrow band imaging can help identify the disease changes of the purified mucosal tissue 
3. Inject solution at the submucosal layer to separate the lesions and submucosal layer 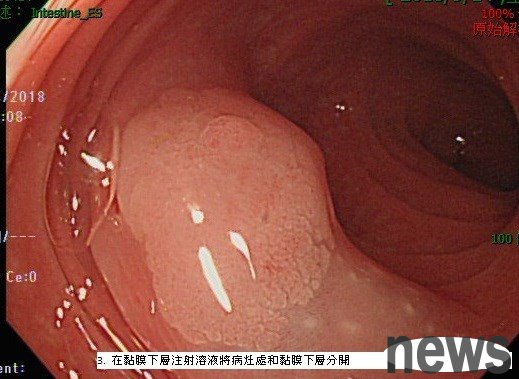
4. Use the internal lens snare to remove the lesions 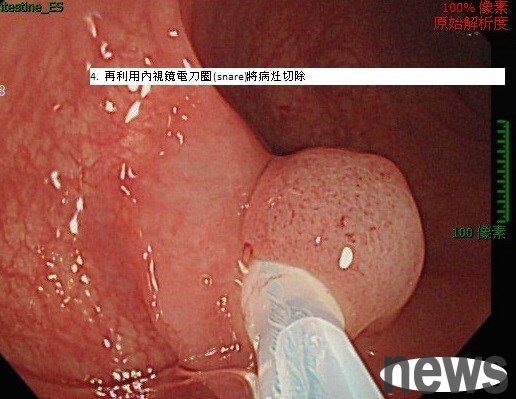
5. There will be a small wound after resection 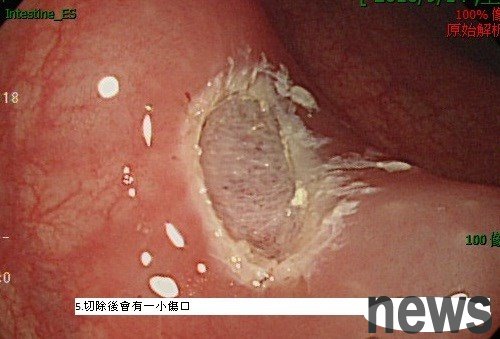
6. Close the wound with the hemostasis clamp to reduce bleeding risks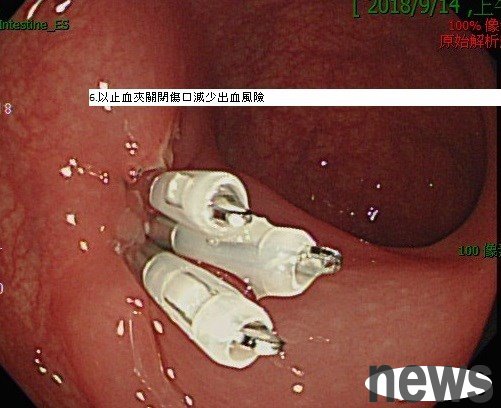
●Author's introduction_Liang Chengchao Medical
Specialist: liver, gastrointestinal disease, internal lens examination and treatment, ultrasound
Current Position: Deputy Dean of Beitou Health Management Hospital, Beitou Hospital,
Study: Scholar from the Institute of Clinical Medicine, Taiwan University, Medical Bachelor from the Institute of Chenggong University,
Study: Department of Internship of National Taiwan University, Inpatient Department of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, General Medical Director, Supersonic and Internal Diagnosis Center, Hospital, Director, Department of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, Hospital, Director, Department of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, Hospital Director of Assistant Professor of the Department of Digestion and Digestion in Taiwan